Features Articles
IPC workmanship standards are getting a definition revamp.
IPC workmanship standards are used throughout the industry, in particular by OEMs and EMS companies as a way to ensure all those involved in producing printed circuit assemblies agree on what’s acceptable and what’s not.
A study of the influence of design parameters that impact success.
A microvia is defined in IPC-T-50M as “a blind structure (as plated) with a maximum aspect ratio of 1:1 when measured in accordance with FIGURE 1, terminating on or penetrating a target land, with a total depth (X) of no more than 0.25mm [0.00984 in] measured from the structure’s capture land foil to the target land.”
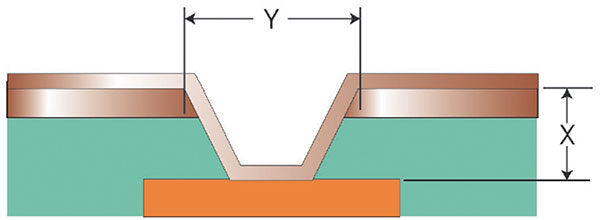
Figure 1. Microvia definition per IPC-T-50M. (Note: X/Y = microvia plating aspect ratio, with X < 0.25mm (0.00984") and aspect ratio < 1:1.)
Advantages to using microvias in PCB design include but are not limited to signal integrity, routing real estate, and pin escape. The most common reason that drives designs to use microvias is the need to escape the pins of a fine-pitch part. As pin pitch on an integrated circuit (IC) is reduced, the design starts to approach a threshold where mechanically drilled vias are not possible. When this happens, other routing solutions such as microvias are required. Use of area array components with a pitch of less than 0.8mm will very likely require the use of microvias to escape the pins of the component, and these components are becoming common in high-reliability electronics such as space hardware and military/defense products. Another advantage is microvias can be used to make connections between two adjacent layers, thus saving a significant amount of routing real estate by not requiring a via that spans multiple layers as a mechanically drilled via typically would. And microvias help with signal integrity of high-speed digital or radio frequency (RF) circuits. At higher frequencies designs can be very sensitive to signal reflection caused by via stubs, and microvias may be required to mitigate signal integrity issues.
Improving problem identification and resolution speed through dual disciplines.

Teams at multiple SigmaTron International facilities have been trained in Lean Six Sigma philosophy. However, some companies work from a pure Lean manufacturing philosophy without Six Sigma tools. This month, we look at the benefits of integrating these disciplines.
The AI-driven world of surveys could use a personal touch.

Those who use ride sharing apps have doubtless noticed the ride is not the complete part of the story. Once you arrive, your app, somewhat intrusively, insists you complete a survey, rating the driver. The survey is Part Two of the journey. One must take care to answer it “correctly.” Inquiries follow if one doesn’t.
Which makes one wonder …
Deep learning (n, int): Techspeak for making something simple, often intuitively obvious, sound more sophisticated than it truly is. Faux profundity.
And ask this: Who gets to define “correctly?”
Further: What qualifies the person doing the defining?
Newly developed, dedicated purpose precision milling machinery simplifies rework.
BGAs, CSPs, flip chips and other component packages on handheld devices are commonplace today in consumer, military, and industrial products such as tablets, smartwatches, and handheld computers. These handheld products, along with transmission control modules, cameras and image sensors in the automotive sector, use underfill to withstand mechanical shock or impact that takes place when devices are dropped or struck. Underfilling these component packages creates a compliant layer between the package and printed circuit board that increases the reliability of the interconnections even when subjected to outside forces.
Underfill is a polymeric material used to fill the gap between the PCB and underside of the electronic component package, thereby surrounding and protecting the solder joints. This material boosts the reliability of the component, which is subject to mechanical impacts and shocks by distributing the forces. Thermal stresses caused by the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatch between the component and PCB are lessened using underfill. Typically, underfills have a high modulus (E) matched CTE with respect to the solder, as well as a high glass transition temperature (Tg). Underfill dampens and distributes the stress more uniformly on the solder joints, thereby increasing interconnection reliability. As pitch of components such as CSPs becomes tighter, the standoff height between the bottom of the device and PCB lessens, thereby reducing the PCB level reliability.1

A “rougher” foil may improve stencil performance.
A high-performing stencil printing process deposits the right amount of material volume in the right place, at the right time, and at the lowest cost per print achievable. Every assembly professional strives for this utopia, leaving no solder paste stuck in the apertures or smeared on the underside of the stencil. Naturally, with all the variables, this state is difficult to achieve 100% of the time. A perfect gasket (board to stencil) does not exist in the electronics manufacturing real world. Transfer efficiency is managed through aperture designs to provide the desired material volume on the pad, and solder paste smear (or its potential) is alleviated by cleaning the underside of the stencil between prints to avoid bridging. Cleaning, of course, comes at a cost – both in consumables use and in production time. If more high-quality prints can be achieved between necessary cleans, consumables overhead will be lower and throughput will be higher.


